HAMi
| English version | 中文版 |

Project-HAMi: Heterogeneous AI Computing Virtualization Middleware
Introduction
HAMi, formerly known as ‘k8s-vGPU-scheduler’, is a Heterogeneous device management middleware for Kubernetes. It can manage different types of heterogeneous devices (like GPU, NPU, etc.), share heterogeneous devices among pods, make better scheduling decisions based on topology of devices and scheduling policies.
It aims to remove the gap between different Heterogeneous devices, and provide a unified interface for users to manage with no changes to their applications. As of December 2024, HAMi has been widely used not only in Internet, public cloud and private cloud, but also broadly adopted in various vertical industries including finance, securities, energy, telecommunications, education, and manufacturing. More than 50 companies or institutions are not only end users but also active contributors.

HAMi is a sandbox and landscape project of
Cloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF),
CNAI Landscape project.
Device virtualization
HAMi provides device virtualization for several heterogeneous devices including GPU, by supporting device sharing and device resource isolation. For the list of devices supporting device virtualization, see supported devices
Device sharing
- Allows partial device allocation by specifying device core usage.
- Allows partial device allocation by specifying device memory.
- Imposes a hard limit on streaming multiprocessors.
- Requires zero changes to existing programs.
- Support dynamic-mig feature, example

Device Resources Isolation
A simple demonstration of device isolation: A task with the following resources will see 3000M device memory inside container:
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1 # declares how many physical GPUs the pod needs
nvidia.com/gpumem: 3000 # identifies 3G GPU memory each physical GPU allocated to the pod
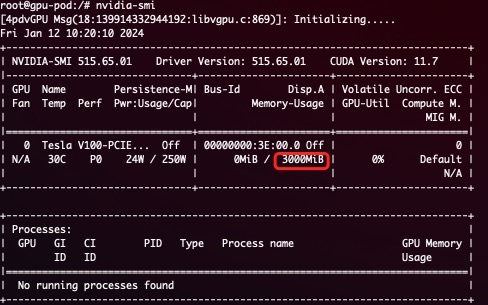
Note:
- After installing HAMi, the value of
nvidia.com/gpuregistered on the node defaults to the number of vGPUs.- When requesting resources in a pod,
nvidia.com/gpurefers to the number of physical GPUs required by the current pod.
Supported devices
NVIDIA GPU
Cambricon MLU
HYGON DCU
Iluvatar CoreX GPU
Moore Threads GPU
HUAWEI Ascend NPU
MetaX GPU
Architecture

HAMi consists of several components, including a unified mutatingwebhook, a unified scheduler extender, different device-plugins and different in-container virtualization technics for each heterogeneous AI devices.
Quick Start
Choose your orchestrator
Prerequisites
The list of prerequisites for running the NVIDIA device plugin is described below:
- NVIDIA drivers >= 440
- nvidia-docker version > 2.0
- default runtime configured as nvidia for containerd/docker/cri-o container runtime
- Kubernetes version >= 1.18
- glibc >= 2.17 & glibc < 2.30
- kernel version >= 3.10
- helm > 3.0
Install
First, Label your GPU nodes for scheduling with HAMi by adding the label “gpu=on”. Without this label, the nodes cannot be managed by our scheduler.
kubectl label nodes {nodeid} gpu=on
Add our repo in helm
helm repo add hami-charts https://project-hami.github.io/HAMi/
Use the following command for deployment:
helm install hami hami-charts/hami -n kube-system
Customize your installation by adjusting the configs.
Verify your installation using the following command:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
If both hami-device-plugin (formerly known as vgpu-device-plugin) and hami-scheduler (formerly known as vgpu-scheduler) pods are in the Running state, your installation is successful. You can try examples here
WebUI
HAMi-WebUI is available after HAMi v2.4
For installation guide, click here
Monitor
Monitoring is automatically enabled after installation. Obtain an overview of cluster information by visiting the following URL:
http://{scheduler ip}:{monitorPort}/metrics
The default monitorPort is 31993; other values can be set using --set devicePlugin.service.httpPort during installation.
Grafana dashboard example
Note The status of a node won’t be collected before you submit a task
Notes
- If you don’t request vGPUs when using the device plugin with NVIDIA images all the GPUs on the machine may be exposed inside your container
- Currently, A100 MIG can be supported in only “none” and “mixed” modes.
- Tasks with the “nodeName” field cannot be scheduled at the moment; please use “nodeSelector” instead.
RoadMap, Governance & Contributing
The project is governed by a group of Maintainers and Contributors. How they are selected and govern is outlined in our Governance Document.
If you’re interested in being a contributor and want to get involved in developing the HAMi code, please see CONTRIBUTING for details on submitting patches and the contribution workflow.
See RoadMap to see anything you interested.
Meeting & Contact
The HAMi community is committed to fostering an open and welcoming environment, with several ways to engage with other users and developers.
If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out to us through the following channels:
- Regular Community Meeting: Friday at 16:00 UTC+8 (Chinese)(weekly). Convert to your timezone.
- Email: refer to the MAINTAINERS.md to find the email addresses of all maintainers. Feel free to contact them via email to report any issues or ask questions.
- mailing list
-
slack Join
Talks and Presentations
| Link | |
|---|---|
| CHINA CLOUD COMPUTING INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPER CONFERENCE (Beijing 2024) | Unlocking heterogeneous AI infrastructure on k8s clusters Starting from 03:06:15 |
| KubeDay(Japan 2024) | Unlocking Heterogeneous AI Infrastructure K8s Cluster:Leveraging the Power of HAMi |
| KubeCon & AI_dev Open Source GenAI & ML Summit(China 2024) | Is Your GPU Really Working Efficiently in the Data Center?N Ways to Improve GPU Usage |
| KubeCon & AI_dev Open Source GenAI & ML Summit(China 2024) | Unlocking Heterogeneous AI Infrastructure K8s Cluster |
| KubeCon(EU 2024) | Cloud Native Batch Computing with Volcano: Updates and Future |
License
HAMi is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.








